Case studies
Social Movement Action Framework
Advocating for supervised injection services to save lives
RNAO advocates for making harm reduction services available for people who use substances as a means of saving lives. To this end, individual and collective actions has resulted in continued access to supervised injection services. Read more in this case study.
RNAO supports making harm reduction services available for people who use substances as a means of saving lives, reducing stigma and building healthy communities. As part of this work, RNAO advocates for using evidence to inform policy in the area of supervised injection services.
When the only supervised injection services site in Canada faced threats of closure by the federal government, RNAO mobilized by engaging members’ support, the media and the public. As part of a coalition, RNAO and others advocated for and participated in a hearing before the Supreme Court of Canada.
As a result of the evidence on the benefits of harm reduction and public interventions advocating for the continued access to supervised injection services, the court ruled that the site should remain open. The victory led to the groundwork for additional supervised injection services to open in other provinces across Canada, including Ontario (Grinspun et al., 2018a).
Promoting healthy public policy through mobilized collective actions
Queen’s Park on the Road and Queen’s Park Day are two events in which RNAO members meet with members of provincial parliament (MPPs) from all of the political parties to promote healthy public policy and nursing services. through individual and collective actions. Learn more in this case study.
Through two annual initiatives – Queen’s Park on the Road and Queen’s Park Day – RNAO members meet with members of provincial parliament (MPPs) from all of the political parties to promote healthy public policy and nursing services. Through direct engagement and advocacy with MPPs, RNAO has mobilized collective action for policy initiatives addressing areas such as poverty reduction, the use of pesticides for cosmetic use, promoting refugee health and protecting the safety and security of residents in long-term care (Grinspun et al., 2018a).

Mobilizing community engagement to sustain a childhood obesity prevention initiative
Multiple communities mobilized to sustain a childhood obesity prevention program through targeted individual and collective action. Read more in this case study.
A community initiative called Sustainable Childhood Obesity Prevention through Community Engagement (SCOPE) provides an example of collective action in the context of public health.
In the SCOPE public health initiative, the community formed a coalition with local partners such as libraries and primary care offices to take collective action for the prevention of childhood obesity. Together, they participated in a range of collective action activities, including: presentations and events promoting healthy eating choices, stakeholder engagement, resource development and policy and practice change (Kennedy et al., 2019a).

Knowledge-to-Action Framework
Applying the Knowledge-to-Action Framework to reduce wound infections at Perley Health
A case study on reducing wound infections at Perley Health in Ottawa, Ontario to advance best practices using the Knowledge-to-Action framework.
Perley Health is a designate Long-Term Care Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) which demonstrates a strong commitment to providing evidence-based care. During the pandemic, the team identified skin and wound infection as a clinical concern among their residents. Consistent with the literature, residents at Perley Health experiencing comorbid medical conditions such as frailty, diabetes, and arterial and venous insufficiency were at increased risk for chronic wound infections [1]. Chronic wounds are a prime environment for bacteria, including biofilm, making wound infection a common problem [2] [3]. Managing biofilm, which can affect wound healing by creating chronic inflammation or infection [3], becomes crucial as up to 80 per cent of infections are caused by this type of bacteria [4] [5].
To adopt and integrate best practices, the team at Perley Health decided to implement the Assessment and Management of Pressure Injuries for the Interprofessional Team best practice guideline (BPG). To support a systematic approach to change, four of the action cycle phases of the Knowledge-to-Action Framework, from the Leading Change Toolkit [6] are highlighted below.

Identify the problem
Perley Health’s wound care protocol was audited and the following gaps were identified based on current evidence:
- Aseptic wound cleansing technic could be improved, as nonsterile gauze was used for wound cleansing.
- Wound cleaning solution was not effective to manage microbial load in chronic wounds
- Baseline wound infection data were collected on the number of infected wounds within the organization each month over three years and is ongoing
Adapt to local context
The project was supported by key formal and informal leaders within the organization including the Nurse Specialized in Wounds, Ostomy and continence (NSWOC), the Director of Clinical Practice, a team of wound care champions, the IPAC team and material management. Staff was motivated to improve resident outcomes by lowering infection rates which facilitated the project but many continued to use old supplies so as to not waste material. Providing the rationale for the change and associated best practices improved knowledge uptake, as did removing old supplies to cut down on confusion. Barriers the team encountered included staff turnover and educating new team members.
Select, tailor, implement interventions
The interventions listed below were selected, tailored and implemented based on the evidence that was adapted to the local context. They were purposely chosen to support the clinical teams’ needs on busy units and to creatively overcome staffing challenges. Interventions included:
- use of a wound cleanser containing an antimicrobial
- use of sterile equipment for wound care, including sterile gauze
- creation of a wound-cleansing protocol was created to reflect best practice
- updating and approval of a policy by the Risk Assessment and Prevention of Pressure Ulcers team in collaboration with the director of clinical practice
Perley Health also created and delivered education in two formats designed to be accessible to front-line staff:
- Just-in-Time education was provided on every unit, on every shift, to registered staff by the NSWOC on all shift sets, over a one-month period. Wound care champions were available on each shift to aid in learning and answer additional questions to support the team’s needs.
- A continuing education online learning module was created and uploaded onto Perley Health’s Surge learning platform. Training is included in new hire onboarding and mandatory for yearly education.
Image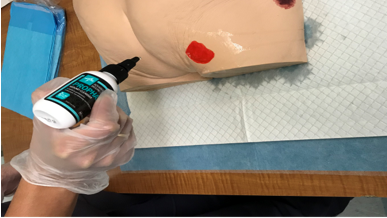
An RPN demonstrating how to cleanse a wound using wound cleanser at Perley Health
Evaluate outcomes
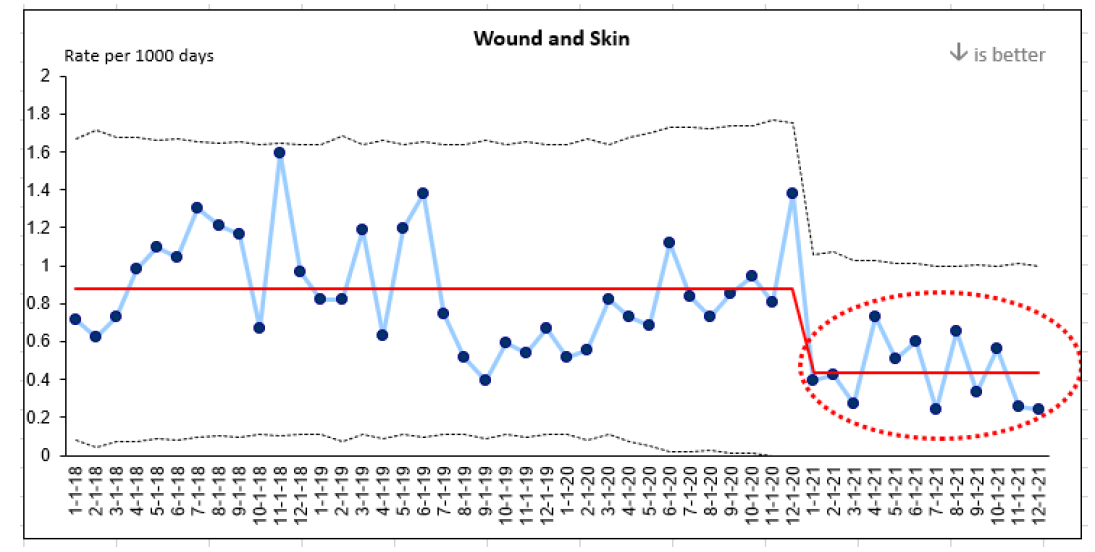
Evaluation indicators were selected to determine the impact of the implementation interventions when compared to baseline data, including the rate of wound and skin infections per 1,000 days. A 50 per cent reduction in wound infections was identified following the implementation of the identified change strategies and education above.
This graph represents four years of data collection on wound infections at Perley Health. Three years of baseline data and one year of post-implementation data are highlighted in red.
References
- Azevedo, M., Lisboa, C., & Rodrigues, A. (2020). Chronic wounds and novel therapeutic approaches. British Journal of Community Nursing, 25 (12), S26-s32.
- Landis, S.J. (2008). Chronic Wound Infection and Antimicrobial Use. Advances in Skin & Wound Care, 21 (11), p 531-540.
- Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario (2016). Clinical best practice guidelines: Assessment and management of pressure injuries for the interprofessional team (3rd ed.). Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario: Toronto, ON.
- Jamal, M., Ahmad, W., Andleeb, S., Jalil, F., Imran, M., Nawaz. M., Hussain, T., Ali, M., Rafiq, M., & Kamil, M.A. (2018). Bacterial biofilm and associated infections. J Chin Med Assoc. 81(1): 7-11.
- Murphy, C., Atkin, L., Swanson, T., Tachi, M., Tan, Y.K., De Ceniga, M.V., Weir, D., Wolcott, R., Ĉernohorská, J., Ciprandi, G., Dissemond, J., James, G.A., Hurlow, J., Lázaro MartÍnez, J.L., Mrozikiewicz-Rakowska, B., & Wilson, P. (2020). Defying hard-to-heal wounds with an early antibiofilm intervention strategy: wound hygiene. J Wound Care, (Sup3b):S1-S26.
- Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario (2022). Leading change toolkit: Knowledge-to-action framework. https://rnao.ca/leading-change-toolkit Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario: Toronto, ON.

Overcoming barriers to evidence-based practice – Lessons learned from DongZhiMen Hospital and Beijing University of Chinese Medicine (BUCM) School of Nursing
DongZhiMen Hospital and Beijing University of Chinese Medicine (BUCM) School of Nursing are international BPSOs in Beijing, China. Staff at the sites identified barriers to the use of evidence in practice including heavy workloads, cultural differences and reluctant attitudes about using evidence to inform practice.
DongZhiMen Hospital and Beijing University of Chinese Medicine (BUCM) School of Nursing are international BPSOs in Beijing, China. They identified barriers to the use of evidence in practice including heavy workloads, cultural differences and reluctant attitudes about using evidence to inform practice. The assessment and identification of barriers allowed change teams to develop effective strategies for implementation with the input of stakeholders.
For example, for the implementation of the RNAO best practice guideline Assessment and management of foot ulcers for people with diabetes, barriers included
- nursing shortages across China,
- a lack of training to support the development of knowledge and skills in evidence-based nursing practice,
- the costs of guideline implementation. and
- practice recommendations that exceeded local nursing scope.
SOURCE: Transforming Nursing Through Knowledge, 2018.

Facilitating an evidence-based culture at Unity Health Toronto - St. Michael’s Hospital
Unity Health Toronto - St. Michael’s Hospital, a Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) has embedded evidence-based practices into its culture and daily work processes as part of its corporate strategy.
Unity Health Toronto - St. Michael’s Hospital, a Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) in Toronto, Canada, has embedded evidence-based practices into its culture and daily work processes. Evidence-based practice is part of the hospital’s corporate strategy. It has invested resources to build a critical mass (over 30 per cent) of staff members who are best practice champions.

The hospital also provides multiple capacity-building opportunities, including a community of practice, boot camps, booster sessions and mentorship. The annual Nursing Week Gallery Walk, depicted in the image above, is just one way that St. Michael’s Hospital profiles the work of champions and others dedicated to using evidence to inform change initiatives.
SOURCE: Transforming Nursing Through Knowledge, 2018.

Engaging Persons with Lived Experiences
Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital: Co-designing change through the active engagement of persons with lived experience
A case study from Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital focused on engaging persons with lived experience in a change process.
Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital (hereafter referred to as Holland Bloorview) is a designated Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Holland Bloorview has an award-winning Family Leadership Program (FLP), through which family leaders partner with the organization and the Bloorview Research Institute to co-design, shape, and improve services, programs, and policies. Family leaders are families and caregivers who have received services at Holland Bloorview, and have lived experiences of paediatric disability. Family leaders’ roles include being a mentor to other families, an advisor to committees and working groups, and faculty who co-teach workshops to students and other families.
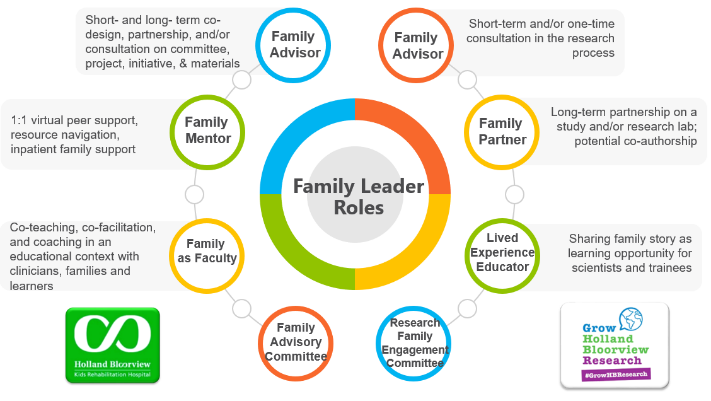
Family Leader Roles at Holland Bloorview. Photo provided with permission by Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital.
The ENFit™ Working Group is an example of a successful implementation co-design process within Holland Bloorview. The ENFit™ Working Group is an interprofessional team working on the adoption of a new type of connection on products used for enteral feeding [feeding directly through the stomach or intestine via a tube]. By introducing the ENFit™ system, a best practice safety standard, the working group plans to reduce the risk of disconnecting the feeding tube from other medical tubes, and thus decrease harm to children and youth who require enteral feeding.
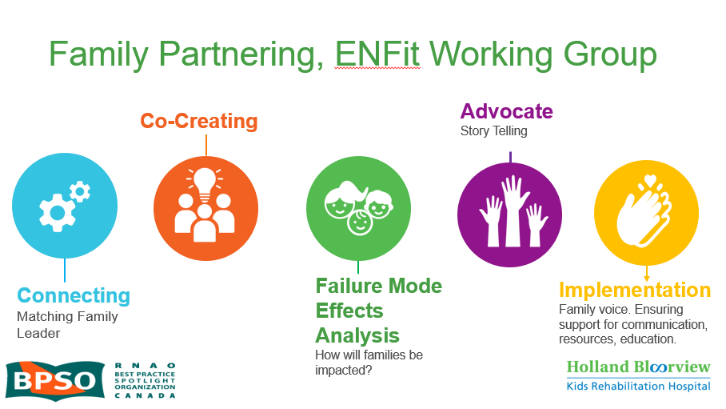
Family Partnering with the EnFit Working Group. Photo provided with permission by Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital.
The working group invited a family member and leader whose son had received services at Holland Bloorview. This family member had significant lived experience with enteral feeding management, enteral medication administration, and other complexities associated with enteral products. During the meetings, great attention was given to the potential impacts on persons and families. The group engaged the family member by:
- co-creating the implementation plan
- involving them in a failure mode affects analysis, which highlighted the impact of the feeding tube supplies on transitions to home, school, and other care settings
- working with the family member to advocate for safe transitions within the provincial pediatric system, which led to the development of the Ontario Pediatric ENFit™ Group
To learn more about Holland Bloorview’s experience in partnering with families in a co-design process, watch their 38-minute webinar: The Power of Family Partnerships.

