Case studies
Social Movement Action Framework
Doodling to frame the issue of poverty
Doodles are a creative expression of framing to position an issue and build meaning. Learn morew in this case study.
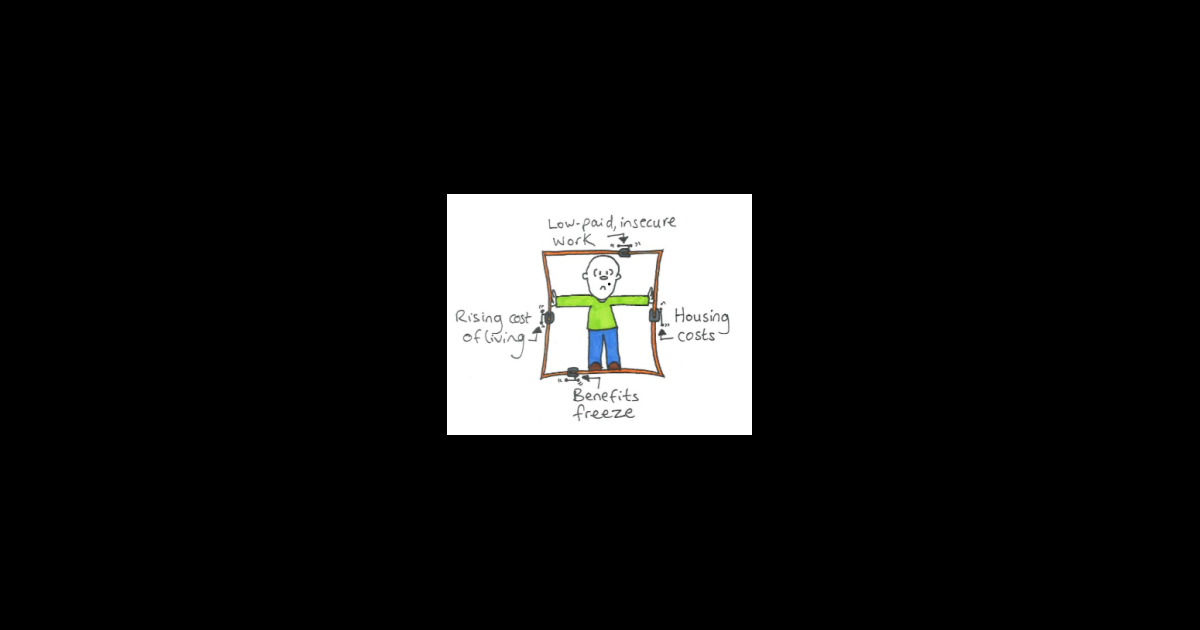
Here is an example of a doodle used to frame the issue of poverty. The notion of people being "locked in" by circumstances outside their control is a powerful metaphor. This doodle shows some of the main factors that combine to restrict and restrain people, locking them into poverty. (Joseph Roundtree Foundation)
Engaging champions' narratives
This RNAO champions training program used storytelling, metaphors, collective artwork and personal narratives to frame the importance of person-and family-centred care. Learn more
This RNAO champions training program used storytelling, metaphors, collective artwork and personal narratives to frame the importance of person-and family-centred care.

Using images and messages for a patient safety campaign
The Canadian Patient Safety Institute’s #ConquerSilence campaign uses images and powerful messaging to frame patient safety issues. Read more in this case study.
The Canadian Patient Safety Institute’s #ConquerSilence campaign uses images and powerful messaging to frame patient safety issues. The campaign includes webinars, podcasts, social media content and a communications toolkit.

Knowledge-to-Action Framework
Sustaining the Assessment and Management of Pain Best Practice Guideline across a multi-site long-term care home
The Region of Peel, a Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®), has sustained the implementation of the Assessment and Management of Pain best practice guideline (BPG) for almost a decade.
The Region of Peel, an RNAO Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) started implementing the RNAO Assessment and Management of Pain best practice guideline (BPG) in 2014 and has sustained its use since then. For example, in their 2019 BPSO annual report, they cited a continuous downward trend in the number of clients who reported a worsening of their pain. Pain experienced by the residents was better controlled, and the staff was found to assess, identify, and manage pain better by using the BPG.
Their keys to success include:
- building on what works (for example, existing practices and policies)
- empowering champions and growing their champion network
- involving residents and families
- gaining support from leaders and partners including RNAO, Peel of Region Leadership, Health Quality Ontario).
- collaborating with an interdisciplinary team
- conducting a formal sustainability evaluation
To learn more about The Region of Peel’s journey in sustaining the use of the Assessing and Managing Pain BPG, along with other BPGs, check out this webinar.

Engaging Persons with Lived Experiences
Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital: Co-designing change through the active engagement of persons with lived experience
A case study from Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital focused on engaging persons with lived experience in a change process.
Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital (hereafter referred to as Holland Bloorview) is a designated Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Holland Bloorview has an award-winning Family Leadership Program (FLP), through which family leaders partner with the organization and the Bloorview Research Institute to co-design, shape, and improve services, programs, and policies. Family leaders are families and caregivers who have received services at Holland Bloorview, and have lived experiences of paediatric disability. Family leaders’ roles include being a mentor to other families, an advisor to committees and working groups, and faculty who co-teach workshops to students and other families.
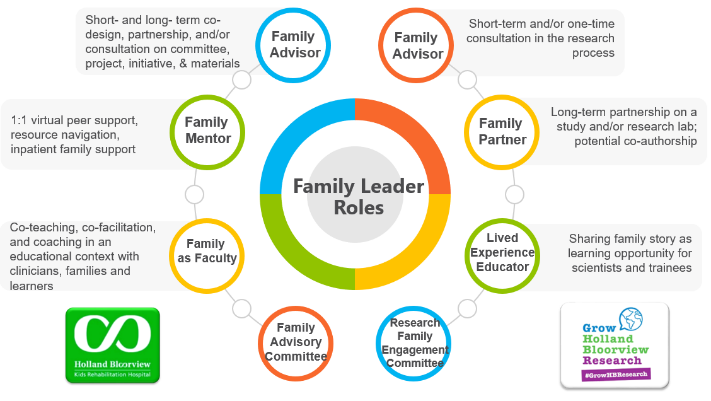
Family Leader Roles at Holland Bloorview. Photo provided with permission by Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital.
The ENFit™ Working Group is an example of a successful implementation co-design process within Holland Bloorview. The ENFit™ Working Group is an interprofessional team working on the adoption of a new type of connection on products used for enteral feeding [feeding directly through the stomach or intestine via a tube]. By introducing the ENFit™ system, a best practice safety standard, the working group plans to reduce the risk of disconnecting the feeding tube from other medical tubes, and thus decrease harm to children and youth who require enteral feeding.
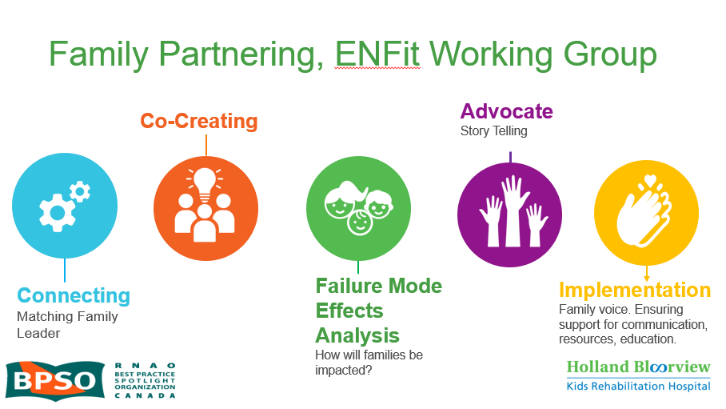
Family Partnering with the EnFit Working Group. Photo provided with permission by Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital.
The working group invited a family member and leader whose son had received services at Holland Bloorview. This family member had significant lived experience with enteral feeding management, enteral medication administration, and other complexities associated with enteral products. During the meetings, great attention was given to the potential impacts on persons and families. The group engaged the family member by:
- co-creating the implementation plan
- involving them in a failure mode affects analysis, which highlighted the impact of the feeding tube supplies on transitions to home, school, and other care settings
- working with the family member to advocate for safe transitions within the provincial pediatric system, which led to the development of the Ontario Pediatric ENFit™ Group
To learn more about Holland Bloorview’s experience in partnering with families in a co-design process, watch their 38-minute webinar: The Power of Family Partnerships.

