Case studies
Social Movement Action Framework
Applying focused strategies and training to achieve a timely change
Staff at the Birchmount and General site locations of Scarborough Health Network in Toronto, Ontario, Canada are committed to providing excellence in clinical practice. In addition to implementing best practice guidelines focused on clinical care, they have also address healthy workplace environment issues including focusing on anti-bullying. Learn more in this case study.
Staff at the Birchmount and General site locations of Scarborough Health Network (SHN) in Toronto, Ontario, Canada are committed to providing excellence in clinical care. At this Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) Best Practice Spotlight Organization (BPSO) – Scarborough Health Network (shn.ca), there was a strong interest and shared concern from staff and leadership teams on the prevention of bullying in the workplace.
In response, they chose to focus on anti-bullying as an area for improvement. To do so, they implemented the Preventing and Managing Violence in the Workplace Best Practice Guideline (RNAO, 2009). Collaborative efforts from the interprofessional team contributed to developing targeted strategies and training, leading to effective action.

Advancing the global Black Lives Matter movement to end systematic racism
The urgent need to end systemic racism gained international traction following the death of George Floyd. Learn more about how an urgent need for action fosters social movement action in this example.
The urgent need to end systemic racism gained international traction following the death of George Floyd. Support for the global Black Lives Matter movement increased, leading to national and international discussions on structural racism and demands to address long-standing problems of police brutality. Calls to action included defunding the police and a global movement for justice, freedom and liberation.

Transforming long-term care reform
The urgent need to transform long-term care (LTC) in Ontario gained broad support in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic. Read more in this case study.
The urgent need to transform long-term care (LTC) in Ontario gained broad support in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic. The pandemic exposed long-standing system failings. Examples of triggers included:
- an alarming mortality rate resulting from COVID-19 in LTC settings, representing a large majority of COVID-19-related deaths in Ontario
- a scathing report from the Canadian Armed Forces
- devastating stories from families who were separated from loved ones

Knowledge-to-Action Framework
Implementing effective interventions for drug and alcohol use using Screening, Brief Intervention and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT)
Evidence-based interventions to support the development of a screening, brief intervention and referral to treatment (SBIRT) for persons who use drugs and alcohol.
Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT) is endorsed by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration as an effective intervention for drug and alcohol use. SBIRT has been implemented in multiple health-care settings including acute care.
Implementation leaders were asked to identify barriers, facilitators, as well as implementation strategies that would be most helpful. From this review, implementation leaders perceived that providing ongoing consultation to clinicians for using SBIRT, distributing educational materials to clinicians, and conducting audits and providing feedback were the most helpful.
All implementation leaders voiced the value of available training resources, and peer support as they moved through the implementation process.
Implementation leaders felt more confident leading change in the future due to the knowledge and skills they developed during SBIRT implementation. They also learned the importance of leveraging support from other interprofessional team members, such as social workers and clinical educators.
Read more about it here. Learn more about SBIRT here. Or, review our best practice guideline, Engaging Clients Who Use Substances.

Adapting BPG recommendations to a public health context – Insights from Toronto Public Health
Toronto Public Health – a Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) - has adapted several RNAO best practice guidelines (BPGs) to align with a population health approach.
Toronto Public Health – a Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) in Toronto, Canada – has implemented several RNAO best practice guidelines (BPGs), including Woman Abuse: Screening, Identification and Initial Response (2005) and Preventing and Addressing Abuse and Neglect of Older Adults (2014). Because some practice recommendations in these guidelines focus on the individual person or patient level, they didn’t always align with Toronto Public Health’s population health approach.
To adapt recommendations to the public health context, the change team completed a literature review to explore definitions and adapt strategies to align with the model of care delivery and health promotion philosophy.
Another approach that was taken by Toronto Public Health: piloting BPG recommendations within one small program team. The team would then evaluate the implementation until successful, consistent with the Plan-Do-Study-Act approach). Once successful, the intervention was scaled up within the organization to other programs and teams (Timmings et al., 2018).

Adapting BPG recommendations to a Chinese acute care context to reform care delivery– lessons learned from DongZhiMen Hospital
Care practices were revised using adapted evidence-based best practice guidelines in an acute care facility in Beijing, China.
DongZhiMen Hospital – a BPSO in Beijing China – was motivated to reform care delivery through the use of RNAO BPGs. While best practice recommendations provided general guidance, DongZhimen Hospital identified the need to translate these statements into detailed instructions and parameters tailored to their specific hospital context.
To adapt statements to their context, they translated the guideline into Chinese. A multidisciplinary team then worked through the initial steps of the Knowledge-to-Action Framework. This involved:
- reviewing carefully the evidence to thoroughly understand the intent of the recommendations
- conducting a comprehensive gap analysis
- interviewing staff members and others to identify facilitators and barriers to the use of the BPG.
Using this information, the team was able to create specific, clinical nursing practice standards derived from the recommendations and relevant to their context (Hailing and Runxi, 2018).

Engaging Persons with Lived Experiences
Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital: Co-designing change through the active engagement of persons with lived experience
A case study from Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital focused on engaging persons with lived experience in a change process.
Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital (hereafter referred to as Holland Bloorview) is a designated Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Holland Bloorview has an award-winning Family Leadership Program (FLP), through which family leaders partner with the organization and the Bloorview Research Institute to co-design, shape, and improve services, programs, and policies. Family leaders are families and caregivers who have received services at Holland Bloorview, and have lived experiences of paediatric disability. Family leaders’ roles include being a mentor to other families, an advisor to committees and working groups, and faculty who co-teach workshops to students and other families.
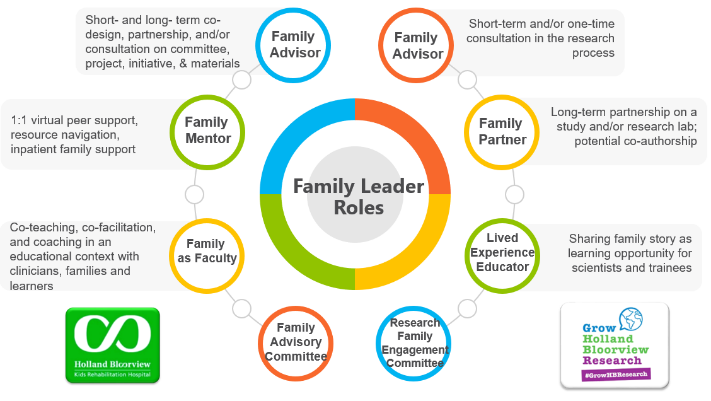
Family Leader Roles at Holland Bloorview. Photo provided with permission by Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital.
The ENFit™ Working Group is an example of a successful implementation co-design process within Holland Bloorview. The ENFit™ Working Group is an interprofessional team working on the adoption of a new type of connection on products used for enteral feeding [feeding directly through the stomach or intestine via a tube]. By introducing the ENFit™ system, a best practice safety standard, the working group plans to reduce the risk of disconnecting the feeding tube from other medical tubes, and thus decrease harm to children and youth who require enteral feeding.
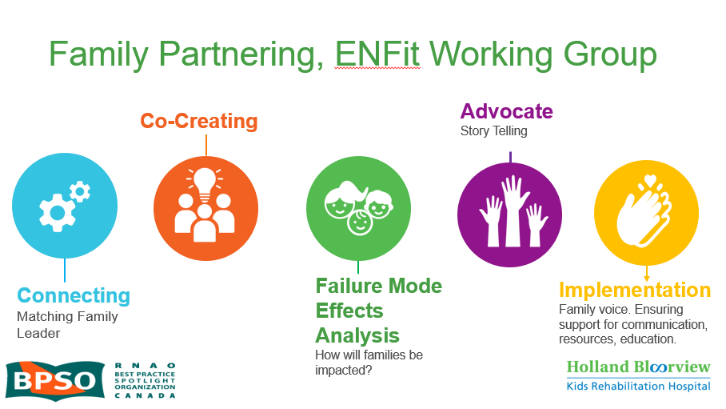
Family Partnering with the EnFit Working Group. Photo provided with permission by Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital.
The working group invited a family member and leader whose son had received services at Holland Bloorview. This family member had significant lived experience with enteral feeding management, enteral medication administration, and other complexities associated with enteral products. During the meetings, great attention was given to the potential impacts on persons and families. The group engaged the family member by:
- co-creating the implementation plan
- involving them in a failure mode affects analysis, which highlighted the impact of the feeding tube supplies on transitions to home, school, and other care settings
- working with the family member to advocate for safe transitions within the provincial pediatric system, which led to the development of the Ontario Pediatric ENFit™ Group
To learn more about Holland Bloorview’s experience in partnering with families in a co-design process, watch their 38-minute webinar: The Power of Family Partnerships.

