Case studies
Social Movement Action Framework
Using social media to increase public visibility and raise awareness
Social media is used by RNAO regularly to advocate for advancing the rights of Ontarians, including residents of long-term care homes. Read this case study that includes examples of effective social media campaigns advocating for the Nursing home Basic Care Guarantee.
RNAO uses social media campaigns to increase public visibility and raise awareness of issues. One example: RNAO’s call on the Ontario government to mandate recommendations set out in its Nursing Home Basic Care Guarantee. The campaign incorporated the hashtags #LTC #BasicCareGuarantee and #4Hours4Seniors to raise awareness of the staffing crisis in long-term care (LTC) and to encourage the public, health professionals, the government, LTC residents and their families to mobilize change.
As the campaign evolved, so did the visuals and the messaging. The three examples below show the stages of the campaign as it gained attention and momentum – from “good” through “better” to “best.”
RNAO developed an Action Alert (AA) to mobilize collective action to advocate for nursing home residents. The link to the AA, the graphic, the messaging and the hashtag #4Hours4Seniors were all shared on social media to urge others to sign and share the AA. People were also encouraged to use the hashtag to contribute to the dialogue about the LTC crisis.
The social media campaign aimed to support the goal set out in the AA – encourage as many people as possible to add their signatures to urge action from key political leaders.
This is a good example of a social media campaign, incorporating a graphic, supportive messaging, a call-to-action (the link to the AA) and a specific hashtag.
In this example, RNAO staff members are holding signs identifying why #4Hours4Seniors matters to them. The hashtag is used consistently and individual reasons for supporting the cause are illustrated.
This is a better example of a social media campaign – it brings a personal touch to the campaign and allows supporters to share why they want to join the conversation. It also brought life to the hashtag and to the purpose of the campaign.
Image
In this example, RNAO collaborated with F.J. Davey Home in Sudbury, Ontario, Canada to encourage residents to share their “why” for wanting #4Hours4Seniors. Building on the same idea as the “better” example given above, this example truly brought a face to the reason for the campaign in the first place. RNAO shared the photos and quotes from residents on its social media feeds (Instagram, Facebook and Twitter) alongside the hashtag #4Hours4Seniors.
For example, M. Doan, a senior living at the F.J. Davey Home, shared: “I am a very independent person, but my wife on the other hand isn’t and she means the world to me. With four hours of care, it doesn’t need to be rushed. And who wouldn’t want to see her beautiful smile for four hours!" (https://twitter.com/RNAO/status/1336781022780928000).
The photos are powerful as they show a real-life married couple living in a LTC home – two of the many residents RNAO advocated for through its AA and its ongoing call for a Nursing Home Basic Care Guarantee. The posters held by the couple express their personal values of dignity and comfort.

Valuing the need for hospice and palliative care services
Advocacy for humane death and dying care practices led to the valuing and realization of hospice and palliative care services in South Australia.
Advocacy for humane death and dying care practices led to the valuing and realization of hospice and palliative care services in South Australia in the 1990s (Elsey, 1998). Early hospice and palliative care advocates pressed for comprehensive community services provided by knowledgeable, humane and compassionate care providers who understood and supported the need for an alternative to medical practices in this area.
Advocates also recognized the need for funding, legislation, support of relevant volunteer organizations, and capacity-building in health professionals to ensure effective delivery of hospice and palliative care services.

Rooting the Kahnawake Schools Diabetes Prevention Project in Indigenous values
A diabetes prevention project in a First Nations community in Quebec was effectively implemented through multiple strategies including the integration of Indigenous values and beliefs.
The Kahnawake Schools Diabetes Prevention Project (ksdpp.org) in the First Nations reserve of the Mohawks of the Kahnawake in Quebec, Canada aims to prevent type 2 diabetes in Kahnawake by empowering community members to care for their health. Project leaders were informed at the outset by evidence that demonstrated a two-fold higher risk of diabetes and diabetes-related complications in adults (Tremblay et al., 2018).
To be meaningful for community members, the change was rooted in the values and traditions of Kanien’kehá:ka beliefs, incorporating a holistic approach of spiritual, emotional, physical and mental dimensions that reflect wellbeing. The project’s focus aligned with the value of protecting and promoting the health of future generations. By linking the change in values, families and other community members were more invested in the cause.

Knowledge-to-Action Framework
Sustaining the Assessment and Management of Pain Best Practice Guideline across a multi-site long-term care home
The Region of Peel, a Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®), has sustained the implementation of the Assessment and Management of Pain best practice guideline (BPG) for almost a decade.
The Region of Peel, an RNAO Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) started implementing the RNAO Assessment and Management of Pain best practice guideline (BPG) in 2014 and has sustained its use since then. For example, in their 2019 BPSO annual report, they cited a continuous downward trend in the number of clients who reported a worsening of their pain. Pain experienced by the residents was better controlled, and the staff was found to assess, identify, and manage pain better by using the BPG.
Their keys to success include:
- building on what works (for example, existing practices and policies)
- empowering champions and growing their champion network
- involving residents and families
- gaining support from leaders and partners including RNAO, Peel of Region Leadership, Health Quality Ontario).
- collaborating with an interdisciplinary team
- conducting a formal sustainability evaluation
To learn more about The Region of Peel’s journey in sustaining the use of the Assessing and Managing Pain BPG, along with other BPGs, check out this webinar.

Engaging Persons with Lived Experiences
Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital: Co-designing change through the active engagement of persons with lived experience
A case study from Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital focused on engaging persons with lived experience in a change process.
Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital (hereafter referred to as Holland Bloorview) is a designated Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Holland Bloorview has an award-winning Family Leadership Program (FLP), through which family leaders partner with the organization and the Bloorview Research Institute to co-design, shape, and improve services, programs, and policies. Family leaders are families and caregivers who have received services at Holland Bloorview, and have lived experiences of paediatric disability. Family leaders’ roles include being a mentor to other families, an advisor to committees and working groups, and faculty who co-teach workshops to students and other families.
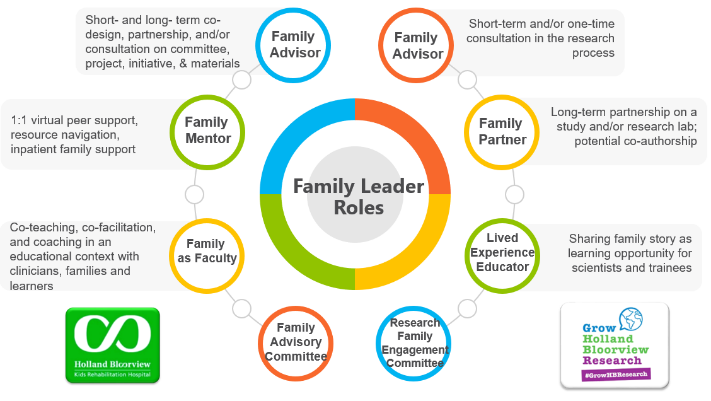
Family Leader Roles at Holland Bloorview. Photo provided with permission by Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital.
The ENFit™ Working Group is an example of a successful implementation co-design process within Holland Bloorview. The ENFit™ Working Group is an interprofessional team working on the adoption of a new type of connection on products used for enteral feeding [feeding directly through the stomach or intestine via a tube]. By introducing the ENFit™ system, a best practice safety standard, the working group plans to reduce the risk of disconnecting the feeding tube from other medical tubes, and thus decrease harm to children and youth who require enteral feeding.
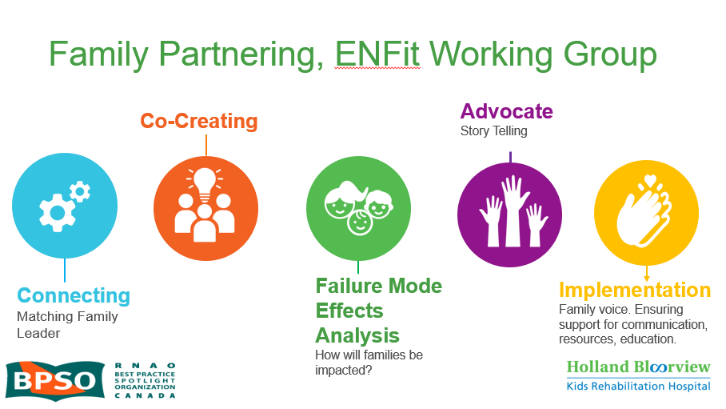
Family Partnering with the EnFit Working Group. Photo provided with permission by Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital.
The working group invited a family member and leader whose son had received services at Holland Bloorview. This family member had significant lived experience with enteral feeding management, enteral medication administration, and other complexities associated with enteral products. During the meetings, great attention was given to the potential impacts on persons and families. The group engaged the family member by:
- co-creating the implementation plan
- involving them in a failure mode affects analysis, which highlighted the impact of the feeding tube supplies on transitions to home, school, and other care settings
- working with the family member to advocate for safe transitions within the provincial pediatric system, which led to the development of the Ontario Pediatric ENFit™ Group
To learn more about Holland Bloorview’s experience in partnering with families in a co-design process, watch their 38-minute webinar: The Power of Family Partnerships.

