Case studies
Social Movement Action Framework
Leveraging transformational leadership to engage teams and enhance person- and family-centred care at Hamilton Haldimand Brant (HNHB) Behavioural Supports Ontario (BSO)
Behavioural Supports Ontario (BSO) is a pre-designate Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) serving long-term care (LTC) homes in Hamilton, Haldimand-Norfolk, Brantford, Burlington and Niagara Regions. Learn more about how they leveraged leadership to engage teams in person- and family-centred care in this case study.
Behavioural Supports Ontario (BSO) is a pre-designate Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) serving long-term care (LTC) homes in Hamilton, Haldimand-Norfolk, Brantford, Burlington and Niagara Regions. BSO aims to enhance care and services for older adults with dementia, complex neurological conditions and mental health challenges who present with responsive behaviours through comprehensive assessment and the development of strategies to optimize care for the resident.
The Hamilton Niagara Haldimand Brant (HNHB) BSO team supports 86 LTC homes with more than 11,200 beds combined. Using transformational leadership and applying key characteristics from the Social Movement Action (SMA) Framework, the organization successfully shifted the culture of the organization to one that supports and sustains high quality and best practices by engaging and motivating staff. Integral to the process was a strong core leadership team of interprofessional staff, intrinsic motivation and momentum.
The organization used RNAO’s BPSO model and gap (opportunity) analysis tools to identify and evaluate areas of improvement in process and practice in three fields of work during the implementation of three RNAO best practice guidelines (BPG) – Person and Family Centered Care, Identification and Assessment of Pain and the Management of Delirium, Dementia and Depression. The impact on personalized care and satisfaction with care are described in Figures 1 and 2.
Figure 1: Percentage of residents and families participating in developing their personalized plan of care (assessments completed during referrals)
Evaluation impact: There was a 50.3 per cent increase in residents’ and families’ participation in developing personalized care plans. Data remained consistently above the HNHB average since January 2021.
Figure 2: Number of residents and families satisfied with their involvement in care and treatment planning
Evaluation impact: There was an 80 per cent increase in residents’ and families’ satisfaction with their involvement in the care and treatment plan at the five implementation sites. Survey results from the five implementation sites demonstrated that residents and families responded “always” and “usually” when asked if they were satisfied with their involvement in the care and treatment planning.
In addition to these outcomes, HNHB BSO has identified the following improvements via quantitative data:
- increased number of screenings and assessments for pain completed
- improved consistency in the screening and assessments of delirium, dementia and depression for all clients
- improvement of more than 80 per cent in the number of residents and families satisfied with their involvement in care and treatment planning
Lessons learned
While implementing the BPGs, HNHB BSO discovered several effective strategies, including the following:
- Engaging staff to agree on a common resident-centered goal by developing a “BSO High Five” program. This program recognizes front-line workers who have demonstrated a person-and family-centered approach to care and have motivated other staff to implement and sustain best practices.
- Applying transformational leadership that focused on staff and stakeholder involvement and engaging them throughout the assessment, planning, implementation and evaluation phases of BPG implementation.
- Developing a best practice steering committee that includes formal and informal leaders, staff, and stakeholders. Persons with lived experience are also engaged in the committee to ensure the incorporation of a global perspective into the planning process from the start.
- Ensuring best practices are on all meeting agendas to sustain momentum toward BPG implementation.
- Conducting process and education gap analyses to address areas of improvement as part of a quality improvement project.
- Valuing staff-driven changes and improving synchronization between the project managers and the team to ensure cohesion, a common identity and a shared vision.
- Understanding the importance of going slow and growing the changes to ensure the alignment amongst all staff. This was crucial to the planning and evaluation phases and allowed for the realignment of strategies and approaches, if necessary, during the implementation of projects.
Shared with permission from Hamilton Niagara Haldimand Brant (HNHB) Behavioural Supports Ontario (BSO)

Mobilizing motivated staff, volunteers and physicians to go "green" at St. Joseph's Healthcare Hamilton
A group of volunteers, staff and physicians from St. Joseph’s Healthcare Hamilton, an acute care facility in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada engaged in a social movement to address environmental issues. This was due in part to the intrinsic motivation of these individuals and their collective energy for change.
A group of volunteers, staff and physicians from St. Joseph’s Healthcare Hamilton, an acute care facility in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada engaged in a social movement to address environmental issues, such as carbon emissions (Herechuk et al., 2010). The change agents formed a team of grassroots activists called the Environmental Vision and Action. They were intrinsically motivated as environmental stewards to make sure changes were made that aligned with environmental determinants of health. Through the support of the hospital’s senior leadership team, the hospital went “green” with environmentally-driven organizational changes, including the creation of a model for environmental excellence. For more details, see Achieving environmental excellence through a multidisciplinary grassroots movement - ScienceDirect

Championing clinical excellence through intrinsic motivation at Vall d'Hebron Barcelona Hospital Campus
Vall d’Hebron Barcelona Hospital Campus championed clinical excellence through nurses' and other staff's leadership and intrinsic motivation.
In Barcelona, Spain, Vall d’Hebron Barcelona Hospital Campus, a Best Practice Spotlight Organization®(BPSO®) Nursing care | Vall d'Hebron Barcelona Hospital Campus (vallhebron.com), nurses and other staff became RNAO Best Practice Champions in several clinical areas including breastfeeding, ostomy and wound care. A ceremony was held to recognize the champions’ leadership and their commitment to using evidence-based guidelines to achieve excellence in clinical practice. Their intrinsic motivation is evidenced by their dedication to providing best practices and optimizing their patients’ health and well-being. For more information, watch the video BPSO Program: Excellence in Cares of Infirmary - YouTube
Knowledge-to-Action Framework
Implementing effective interventions for drug and alcohol use using Screening, Brief Intervention and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT)
Evidence-based interventions to support the development of a screening, brief intervention and referral to treatment (SBIRT) for persons who use drugs and alcohol.
Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT) is endorsed by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration as an effective intervention for drug and alcohol use. SBIRT has been implemented in multiple health-care settings including acute care.
Implementation leaders were asked to identify barriers, facilitators, as well as implementation strategies that would be most helpful. From this review, implementation leaders perceived that providing ongoing consultation to clinicians for using SBIRT, distributing educational materials to clinicians, and conducting audits and providing feedback were the most helpful.
All implementation leaders voiced the value of available training resources, and peer support as they moved through the implementation process.
Implementation leaders felt more confident leading change in the future due to the knowledge and skills they developed during SBIRT implementation. They also learned the importance of leveraging support from other interprofessional team members, such as social workers and clinical educators.
Read more about it here. Learn more about SBIRT here. Or, review our best practice guideline, Engaging Clients Who Use Substances.

Adapting BPG recommendations to a public health context – Insights from Toronto Public Health
Toronto Public Health – a Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) - has adapted several RNAO best practice guidelines (BPGs) to align with a population health approach.
Toronto Public Health – a Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) in Toronto, Canada – has implemented several RNAO best practice guidelines (BPGs), including Woman Abuse: Screening, Identification and Initial Response (2005) and Preventing and Addressing Abuse and Neglect of Older Adults (2014). Because some practice recommendations in these guidelines focus on the individual person or patient level, they didn’t always align with Toronto Public Health’s population health approach.
To adapt recommendations to the public health context, the change team completed a literature review to explore definitions and adapt strategies to align with the model of care delivery and health promotion philosophy.
Another approach that was taken by Toronto Public Health: piloting BPG recommendations within one small program team. The team would then evaluate the implementation until successful, consistent with the Plan-Do-Study-Act approach). Once successful, the intervention was scaled up within the organization to other programs and teams (Timmings et al., 2018).

Adapting BPG recommendations to a Chinese acute care context to reform care delivery– lessons learned from DongZhiMen Hospital
Care practices were revised using adapted evidence-based best practice guidelines in an acute care facility in Beijing, China.
DongZhiMen Hospital – a BPSO in Beijing China – was motivated to reform care delivery through the use of RNAO BPGs. While best practice recommendations provided general guidance, DongZhimen Hospital identified the need to translate these statements into detailed instructions and parameters tailored to their specific hospital context.
To adapt statements to their context, they translated the guideline into Chinese. A multidisciplinary team then worked through the initial steps of the Knowledge-to-Action Framework. This involved:
- reviewing carefully the evidence to thoroughly understand the intent of the recommendations
- conducting a comprehensive gap analysis
- interviewing staff members and others to identify facilitators and barriers to the use of the BPG.
Using this information, the team was able to create specific, clinical nursing practice standards derived from the recommendations and relevant to their context (Hailing and Runxi, 2018).

Engaging Persons with Lived Experiences
Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital: Co-designing change through the active engagement of persons with lived experience
A case study from Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital focused on engaging persons with lived experience in a change process.
Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital (hereafter referred to as Holland Bloorview) is a designated Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Holland Bloorview has an award-winning Family Leadership Program (FLP), through which family leaders partner with the organization and the Bloorview Research Institute to co-design, shape, and improve services, programs, and policies. Family leaders are families and caregivers who have received services at Holland Bloorview, and have lived experiences of paediatric disability. Family leaders’ roles include being a mentor to other families, an advisor to committees and working groups, and faculty who co-teach workshops to students and other families.
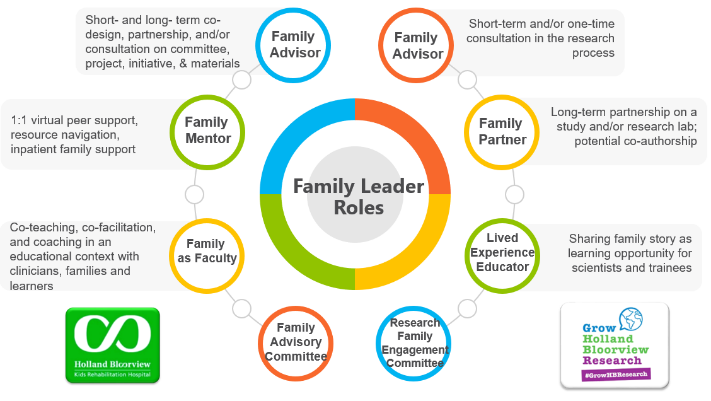
Family Leader Roles at Holland Bloorview. Photo provided with permission by Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital.
The ENFit™ Working Group is an example of a successful implementation co-design process within Holland Bloorview. The ENFit™ Working Group is an interprofessional team working on the adoption of a new type of connection on products used for enteral feeding [feeding directly through the stomach or intestine via a tube]. By introducing the ENFit™ system, a best practice safety standard, the working group plans to reduce the risk of disconnecting the feeding tube from other medical tubes, and thus decrease harm to children and youth who require enteral feeding.
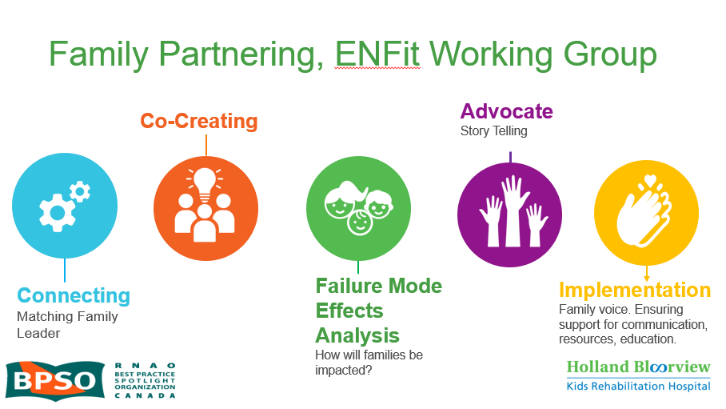
Family Partnering with the EnFit Working Group. Photo provided with permission by Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital.
The working group invited a family member and leader whose son had received services at Holland Bloorview. This family member had significant lived experience with enteral feeding management, enteral medication administration, and other complexities associated with enteral products. During the meetings, great attention was given to the potential impacts on persons and families. The group engaged the family member by:
- co-creating the implementation plan
- involving them in a failure mode affects analysis, which highlighted the impact of the feeding tube supplies on transitions to home, school, and other care settings
- working with the family member to advocate for safe transitions within the provincial pediatric system, which led to the development of the Ontario Pediatric ENFit™ Group
To learn more about Holland Bloorview’s experience in partnering with families in a co-design process, watch their 38-minute webinar: The Power of Family Partnerships.

