Case studies
Social Movement Action Framework
Strengthening health systems: The experience of the National Health Forum in El Salvador (2009 - 2018)
A nationwide social movement in El Salvador from 2009 to 2018 supported the achievement of the National Health Forum and exemplified goals and outcomes being met by activists. Read more in this case study.
The National Health Forum (NHF), a nationwide popular movement in El Salvador, played a central role in the development of the National Public Health System from 2009 to 2018 (León et al., 2020). It is part of a global movement that aims to build coalitions and networks. The People’s Health Movement (PHM) brought together grassroots health activists, civil society organizations and academic institutions from around the world to address the social, environmental, and economic determinants of health (Kapilashrami et al., 2016).
The NHF provides a strong example of community participation and exemplifies a social movement with fully achieved goals. Formally created in 2010, the NHF had three fundamental goals that were met via social movement actions:
- to build people’s power and strengthen the organizational fabric
- to stand against the idea that previous governments held of privatizing health care
- to stimulate and promote effective social participation in health
The NHF developed three community participation strategies that played a role in strengthening El Salvador’s national public health system. These strategies are: (1) building capacity among local community leaders to become effective decision-makers at all levels of the health-care system, (2) responding to and prioritizing the needs identified by the community for the sector-specific working groups, and (3) advocating for policies based on human rights.
“The NHF was born with high participation of different social movements, all united in the same direction. There were a series of problems, as they wanted to privatize health care […] The NHF was created when the health reform came into being. We, the NHF, are part of the reform” – NHF member

Advocating for change through the Alzheimer's Association
The Alzheimer's Association was started by activists committed to advancing Alzheimer's knowledge through research.
The Alzheimer’s Association (Alzheimer's Association | Alzheimer's Disease & Dementia Help) was founded in 1980 by a group of family care providers and individuals who supported the need for an organization dedicated to support the needs of caregivers facing Alzheimer’s and to advance knowledge through research. As early activists for the Alzheimer’s movement, they sought to break down the silence of Alzheimer’s and learn more about the disease, including prevention, treatment and a cure.
Through a people-led approach, the association reaches millions of people globally through a multi-pronged approach grounded in individual and collective action. Advocacy to give all persons living with Alzheimer’s access to the support services they need includes strategies such as launching awareness campaigns and grassroots campaigns to impact legislation.
With multiple chapters throughout North America and globally, the Alzheimer’s Association includes a network of advocates and allies. These include other Alzheimer’s organizations, universities engaged in research, corporations and pharmaceuticals. As an example of a civil society organization, the Alzheimer’s Association is a community-based non-profit organization that has protected and advocated for the needs and interests of persons and families living with Alzheimer’s for over 40 years.

Scaling up change to address hunger and food waste through The Campus Kitchens Project
The Campus Kitchens Project was an effective scaled up change initiative that addressed food insecurity. read more in this case study.
The Campus Kitchens Project (CKP) is an example of a successful scaled-up change initiative. Founded in 2001 as a branch of a community kitchen initiative that targeted food insecurity in Washington, D.C., United States, this non-profit is the first and largest student-led social movement taking on the crisis of food waste and hunger in the United States (Larson et al., 2017). More than 30,000 students in 63 universities, colleges and high schools are now repurposing unwanted or surplus food to provide meals to people who have food insecurity.
Working in leadership teams, student leaders and volunteers on campuses receive education, training and coaching over a period of several months to help empower people, families and communities on topics including:
- food insecurity
- improving social and nutritional health by increasing food knowledge and helping others developing cooking skills
The Campus Kitchen Project also establishes community partnerships with existing local organizations that provide services and food to individuals already challenged with food insecurity, such as senior housing facilities, youth outreach groups and churches. Local leadership teams also partner with dining services that operate large foodservice kitchens and dining halls and engage student groups and faculty advisors.
Student teams carry out different functions. While some teams focus on improving the way that homeless shelters prepare and deliver meals, other teams host communal dinners, partner with senior centers, or improve transportation to improve access to food.
“Instead of more branch offices or trying to provide all the services in-house, we find universities and students to partner with who already have the necessary resources on campus and want to do this kind of community impact work. Turning our nation’s institutions of higher education into hubs for replication and ongoing innovation could be the superhighway to scaling up for any nonprofit.” - Laura Toscano, Director, The Campus Kitchens Project

Knowledge-to-Action Framework
Conducting gap analyses to successfully implement new clinical practices at Tilbury Manor
Tilbury Manor, a long-term care home, chose to focus on provincially-mandated “required programs” when seeking to improve resident care using a gap analysis.
Tilbury Manor, a 75-resident long-term care home in Tilbury chose to focus on provincially-mandated “required programs” (fall prevention, skin and wound care, continence care, bowel management and pain management) when seeking to improve resident care.
They conducted a gap analysis to compare their current practices with the best practices outlined in related RNAO best practice guidelines. Their analysis included an assessment of clinical practices, policies and documentation systems. The results of the gap analysis helped them create specific action plans.
Tilbury Manor then formed project teams led by nurses and supported by a team of champions. These teams proceeded to educate staff, implement new clinical practices, conduct care reviews and conduct audits.
Multiple positive outcomes were reported as a result of implementing these best practices including reductions in reports of pain, less use of restraints, and less falls, pressure ulcers and urinary tract infections.

Leveraging innovative quality monitoring - Humber River Hospital
Humber River Hospital is an acute care facility that has used continuous monitoring to determine the impact of BPG implementation and staff performance.
A major acute-care hospital in Toronto, Ontario, Humber River Hospital (now Humber River Health) has used continuous monitoring to determine the impact of their BPG implementation and staff performance.
These tiles, displayed on large screen monitors in a Command Centre (pictured above), are integrated into the daily delivery of care to support physicians, nurses, and other clinical staff. Each row within the tile represents a patient, followed by where they are located. By clicking on a patient, staff can see more information regarding the clinical criteria that put them on the tile.
With every patient, there is an expected time in which the issue should be resolved based on a service level set by the hospital. If the system detects that the process is taking longer than expected, the icon will escalate to amber and then to red, indicating a higher level of alert.
Tiles also include several quality monitoring indicators based on RNAO's best practice guidelines (BPG) related to fall risk intervention, wound and skin management, pain management and delirium management. By centralizing data in the Command Centre, the monitoring indicators empower clinicians so that they can intervene in a timely manner to ensure that best practices are followed.
Read more about this innovative quality monitoring approach here: https://www.hrh.ca/2020/08/04/cc-risk-of-harm/

Evaluating the impact of implementing the Person- and Family-Centred Care Best Practice Guideline at Spectrum Health Care
Spectrum Health Care, a Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) and home health organization, evaluated care outcomes after implementing the Person- and Family-Centred best practice guideline (BPG).
Spectrum Health Care (Spectrum), an RNAO Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®), is a home health organization with more than 200 nursing staff across three locations in the province of Ontario, Canada.
Spectrum chose to implement the 2015 Person- and Family-Centred Care (PFCC) Best Practice Guideline (BPG) to enhance person- and family-centred care and to reduce complaints regarding care. Members of the senior leadership team at Spectrum Health Care led implementation together with Spectrum’s Patient and Family Advisory Council.
To support the practice change, Spectrum used the following implementation interventions:
- Conducting a gap analysis to determine the knowledge/practice gap;
- Holding education sessions for staff on person- and family-centred care best practices;
- Revising their care processes to include review of care plans with the person and/or members of their family
- Surveying staff members on their attitudes about person- and family-centred care via surveys
- Developing staff education on communication strategies to support the assessment of a person’s care needs and care plans.
After implementing these interventions, Spectrum assessed the number of complaints received from persons receiving care per 1,000 care visits and compared that to their baseline.
They found a decrease of 42 per cent of complaints from persons received over an 18-month time period at one of the sites that was implementing the PFCC BPG at Spectrum Health Care.
At another site, an 80 per cent reduction in complaints was found following the staff education intervention.
Data analyses overall indicated that the implementation of the PFCC BPG was highly successful in reducing persons' complaints regarding care.
Read more about Spectrum Health care’s results of implementing the PFCC BPG here: Slide 2 (rnao.ca)

Engaging Persons with Lived Experiences
Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital: Co-designing change through the active engagement of persons with lived experience
A case study from Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital focused on engaging persons with lived experience in a change process.
Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital (hereafter referred to as Holland Bloorview) is a designated Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Holland Bloorview has an award-winning Family Leadership Program (FLP), through which family leaders partner with the organization and the Bloorview Research Institute to co-design, shape, and improve services, programs, and policies. Family leaders are families and caregivers who have received services at Holland Bloorview, and have lived experiences of paediatric disability. Family leaders’ roles include being a mentor to other families, an advisor to committees and working groups, and faculty who co-teach workshops to students and other families.
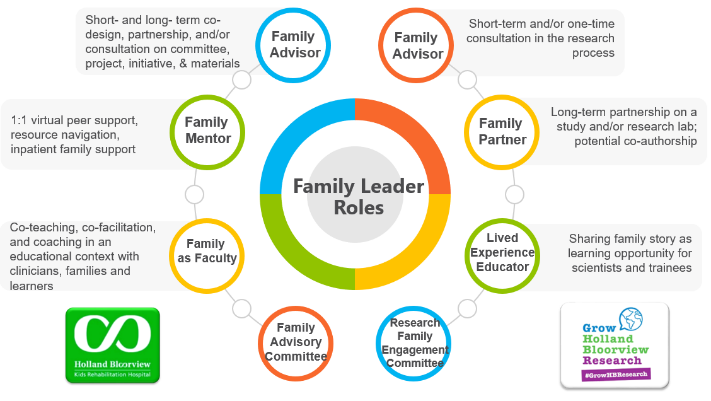
Family Leader Roles at Holland Bloorview. Photo provided with permission by Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital.
The ENFit™ Working Group is an example of a successful implementation co-design process within Holland Bloorview. The ENFit™ Working Group is an interprofessional team working on the adoption of a new type of connection on products used for enteral feeding [feeding directly through the stomach or intestine via a tube]. By introducing the ENFit™ system, a best practice safety standard, the working group plans to reduce the risk of disconnecting the feeding tube from other medical tubes, and thus decrease harm to children and youth who require enteral feeding.
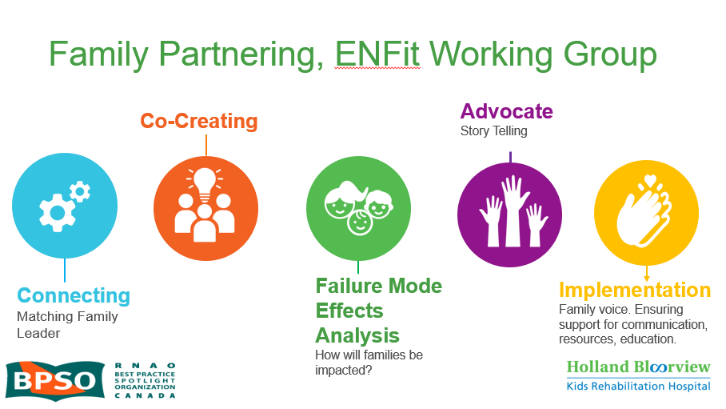
Family Partnering with the EnFit Working Group. Photo provided with permission by Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital.
The working group invited a family member and leader whose son had received services at Holland Bloorview. This family member had significant lived experience with enteral feeding management, enteral medication administration, and other complexities associated with enteral products. During the meetings, great attention was given to the potential impacts on persons and families. The group engaged the family member by:
- co-creating the implementation plan
- involving them in a failure mode affects analysis, which highlighted the impact of the feeding tube supplies on transitions to home, school, and other care settings
- working with the family member to advocate for safe transitions within the provincial pediatric system, which led to the development of the Ontario Pediatric ENFit™ Group
To learn more about Holland Bloorview’s experience in partnering with families in a co-design process, watch their 38-minute webinar: The Power of Family Partnerships.

