Case studies
Social Movement Action Framework
Strengthening health systems: The experience of the National Health Forum in El Salvador (2009 - 2018)
A nationwide social movement in El Salvador from 2009 to 2018 supported the achievement of the National Health Forum and exemplified goals and outcomes being met by activists. Read more in this case study.
The National Health Forum (NHF), a nationwide popular movement in El Salvador, played a central role in the development of the National Public Health System from 2009 to 2018 (León et al., 2020). It is part of a global movement that aims to build coalitions and networks. The People’s Health Movement (PHM) brought together grassroots health activists, civil society organizations and academic institutions from around the world to address the social, environmental, and economic determinants of health (Kapilashrami et al., 2016).
The NHF provides a strong example of community participation and exemplifies a social movement with fully achieved goals. Formally created in 2010, the NHF had three fundamental goals that were met via social movement actions:
- to build people’s power and strengthen the organizational fabric
- to stand against the idea that previous governments held of privatizing health care
- to stimulate and promote effective social participation in health
The NHF developed three community participation strategies that played a role in strengthening El Salvador’s national public health system. These strategies are: (1) building capacity among local community leaders to become effective decision-makers at all levels of the health-care system, (2) responding to and prioritizing the needs identified by the community for the sector-specific working groups, and (3) advocating for policies based on human rights.
“The NHF was born with high participation of different social movements, all united in the same direction. There were a series of problems, as they wanted to privatize health care […] The NHF was created when the health reform came into being. We, the NHF, are part of the reform” – NHF member

Advocating for change through the Alzheimer's Association
The Alzheimer's Association was started by activists committed to advancing Alzheimer's knowledge through research.
The Alzheimer’s Association (Alzheimer's Association | Alzheimer's Disease & Dementia Help) was founded in 1980 by a group of family care providers and individuals who supported the need for an organization dedicated to support the needs of caregivers facing Alzheimer’s and to advance knowledge through research. As early activists for the Alzheimer’s movement, they sought to break down the silence of Alzheimer’s and learn more about the disease, including prevention, treatment and a cure.
Through a people-led approach, the association reaches millions of people globally through a multi-pronged approach grounded in individual and collective action. Advocacy to give all persons living with Alzheimer’s access to the support services they need includes strategies such as launching awareness campaigns and grassroots campaigns to impact legislation.
With multiple chapters throughout North America and globally, the Alzheimer’s Association includes a network of advocates and allies. These include other Alzheimer’s organizations, universities engaged in research, corporations and pharmaceuticals. As an example of a civil society organization, the Alzheimer’s Association is a community-based non-profit organization that has protected and advocated for the needs and interests of persons and families living with Alzheimer’s for over 40 years.

Scaling up change to address hunger and food waste through The Campus Kitchens Project
The Campus Kitchens Project was an effective scaled up change initiative that addressed food insecurity. read more in this case study.
The Campus Kitchens Project (CKP) is an example of a successful scaled-up change initiative. Founded in 2001 as a branch of a community kitchen initiative that targeted food insecurity in Washington, D.C., United States, this non-profit is the first and largest student-led social movement taking on the crisis of food waste and hunger in the United States (Larson et al., 2017). More than 30,000 students in 63 universities, colleges and high schools are now repurposing unwanted or surplus food to provide meals to people who have food insecurity.
Working in leadership teams, student leaders and volunteers on campuses receive education, training and coaching over a period of several months to help empower people, families and communities on topics including:
- food insecurity
- improving social and nutritional health by increasing food knowledge and helping others developing cooking skills
The Campus Kitchen Project also establishes community partnerships with existing local organizations that provide services and food to individuals already challenged with food insecurity, such as senior housing facilities, youth outreach groups and churches. Local leadership teams also partner with dining services that operate large foodservice kitchens and dining halls and engage student groups and faculty advisors.
Student teams carry out different functions. While some teams focus on improving the way that homeless shelters prepare and deliver meals, other teams host communal dinners, partner with senior centers, or improve transportation to improve access to food.
“Instead of more branch offices or trying to provide all the services in-house, we find universities and students to partner with who already have the necessary resources on campus and want to do this kind of community impact work. Turning our nation’s institutions of higher education into hubs for replication and ongoing innovation could be the superhighway to scaling up for any nonprofit.” - Laura Toscano, Director, The Campus Kitchens Project

Knowledge-to-Action Framework
Implementing effective interventions for drug and alcohol use using Screening, Brief Intervention and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT)
Evidence-based interventions to support the development of a screening, brief intervention and referral to treatment (SBIRT) for persons who use drugs and alcohol.
Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT) is endorsed by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration as an effective intervention for drug and alcohol use. SBIRT has been implemented in multiple health-care settings including acute care.
Implementation leaders were asked to identify barriers, facilitators, as well as implementation strategies that would be most helpful. From this review, implementation leaders perceived that providing ongoing consultation to clinicians for using SBIRT, distributing educational materials to clinicians, and conducting audits and providing feedback were the most helpful.
All implementation leaders voiced the value of available training resources, and peer support as they moved through the implementation process.
Implementation leaders felt more confident leading change in the future due to the knowledge and skills they developed during SBIRT implementation. They also learned the importance of leveraging support from other interprofessional team members, such as social workers and clinical educators.
Read more about it here. Learn more about SBIRT here. Or, review our best practice guideline, Engaging Clients Who Use Substances.

Adapting BPG recommendations to a public health context – Insights from Toronto Public Health
Toronto Public Health – a Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) - has adapted several RNAO best practice guidelines (BPGs) to align with a population health approach.
Toronto Public Health – a Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) in Toronto, Canada – has implemented several RNAO best practice guidelines (BPGs), including Woman Abuse: Screening, Identification and Initial Response (2005) and Preventing and Addressing Abuse and Neglect of Older Adults (2014). Because some practice recommendations in these guidelines focus on the individual person or patient level, they didn’t always align with Toronto Public Health’s population health approach.
To adapt recommendations to the public health context, the change team completed a literature review to explore definitions and adapt strategies to align with the model of care delivery and health promotion philosophy.
Another approach that was taken by Toronto Public Health: piloting BPG recommendations within one small program team. The team would then evaluate the implementation until successful, consistent with the Plan-Do-Study-Act approach). Once successful, the intervention was scaled up within the organization to other programs and teams (Timmings et al., 2018).

Adapting BPG recommendations to a Chinese acute care context to reform care delivery– lessons learned from DongZhiMen Hospital
Care practices were revised using adapted evidence-based best practice guidelines in an acute care facility in Beijing, China.
DongZhiMen Hospital – a BPSO in Beijing China – was motivated to reform care delivery through the use of RNAO BPGs. While best practice recommendations provided general guidance, DongZhimen Hospital identified the need to translate these statements into detailed instructions and parameters tailored to their specific hospital context.
To adapt statements to their context, they translated the guideline into Chinese. A multidisciplinary team then worked through the initial steps of the Knowledge-to-Action Framework. This involved:
- reviewing carefully the evidence to thoroughly understand the intent of the recommendations
- conducting a comprehensive gap analysis
- interviewing staff members and others to identify facilitators and barriers to the use of the BPG.
Using this information, the team was able to create specific, clinical nursing practice standards derived from the recommendations and relevant to their context (Hailing and Runxi, 2018).

Engaging Persons with Lived Experiences
Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital: Co-designing change through the active engagement of persons with lived experience
A case study from Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital focused on engaging persons with lived experience in a change process.
Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital (hereafter referred to as Holland Bloorview) is a designated Best Practice Spotlight Organization® (BPSO®) in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Holland Bloorview has an award-winning Family Leadership Program (FLP), through which family leaders partner with the organization and the Bloorview Research Institute to co-design, shape, and improve services, programs, and policies. Family leaders are families and caregivers who have received services at Holland Bloorview, and have lived experiences of paediatric disability. Family leaders’ roles include being a mentor to other families, an advisor to committees and working groups, and faculty who co-teach workshops to students and other families.
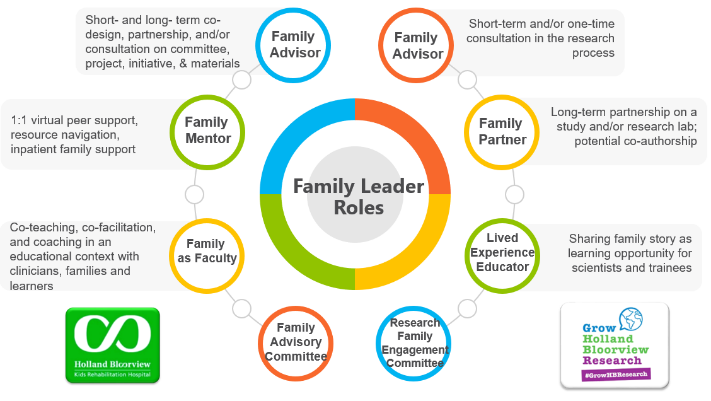
Family Leader Roles at Holland Bloorview. Photo provided with permission by Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital.
The ENFit™ Working Group is an example of a successful implementation co-design process within Holland Bloorview. The ENFit™ Working Group is an interprofessional team working on the adoption of a new type of connection on products used for enteral feeding [feeding directly through the stomach or intestine via a tube]. By introducing the ENFit™ system, a best practice safety standard, the working group plans to reduce the risk of disconnecting the feeding tube from other medical tubes, and thus decrease harm to children and youth who require enteral feeding.
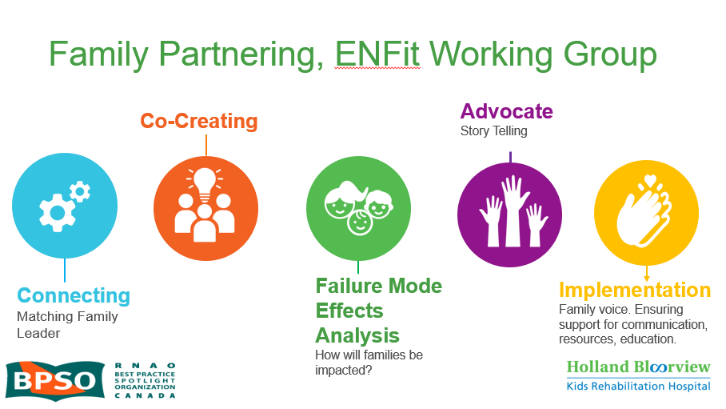
Family Partnering with the EnFit Working Group. Photo provided with permission by Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital.
The working group invited a family member and leader whose son had received services at Holland Bloorview. This family member had significant lived experience with enteral feeding management, enteral medication administration, and other complexities associated with enteral products. During the meetings, great attention was given to the potential impacts on persons and families. The group engaged the family member by:
- co-creating the implementation plan
- involving them in a failure mode affects analysis, which highlighted the impact of the feeding tube supplies on transitions to home, school, and other care settings
- working with the family member to advocate for safe transitions within the provincial pediatric system, which led to the development of the Ontario Pediatric ENFit™ Group
To learn more about Holland Bloorview’s experience in partnering with families in a co-design process, watch their 38-minute webinar: The Power of Family Partnerships.

